See all of our Ammonia Signs
What is Ammonia?
Ammonia is a colorless gas, with a pungent odor. It is widely used as a refrigerant and for the manufacture of products such as pesticides, fertilizer, plastic and other chemicals. Exposure to ammonia in small amounts can cause irritation to the eyes, nose and throat. At higher levels, ammonia may turn fatal due to throat swelling or chemical burns to the lungs. Ammonia can be a highly corrosive chemical. With an it's increased use in recent years as a refrigerant, it is important to ensure worker safety by providing proper safety and hazard identification.
Fire Protection Guide to Hazardous Materials - Edition 14th
| Chemical Name / CAS No. | NFPA 30 / OSHA Class | Flash Point °F (°C) | Health | Flammability | Instability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonia, anhydrous NH3 7664-41-7 |
None | Gas | 3 | 1* | 0 |
*NFPA 49 – This gas is ‘1’ instead of ‘4’ because it is hard to burn.
Why are there different ratings for Ammonia?
The ANSI/IIAR 2–2008 Addendum section 13.1.10.4 states that “Refrigerating systems shall be provided with approved informative signs, emergency signs, charts and labels in accordance with NFPA 704. Hazard signs shall be in accordance with the International Mechanical Code”.
In the case of ammonia refrigeration systems, IMC Table 1103.1 has classified ammonia with health, fire and instability ratings of 3-3-0 for indoor installations and 3-1-0 for outdoor installations. As represented below:
2015 International Mechanical Code (IMC)
Refrigeration System Classification
| Chemical Refrigerant | Formula | Chemical Name of Blend | Refrigerant Classification | Degrees of Hazard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-717 | NH3 | Ammonia | B2f | 3–3–0c |
C: For installations that are entirely outdoors use 3–1–0.
This code was obtained from 2015 International Mechanical CodeOther Hazard Ratings
The other ratings that appear on the Ammonia signs page besides those listed in NFPA's Fire Protection Guide to Hazardous Materials - Edition 14th and IMC above, where found in other documentation.
NFPA 49 Chapter 5 Hazardous Chemical Data Sheet
The Hazardous Chemical Data Compilation, previously known as NFPA 49, provides guidance on the hazards of chemicals to emergency personnel, safety professionals, inspection and enforcement officials on storage and fire fighting techniques that can be used in an emergency or in disaster planning.
Name: AMMONIA, anhydrous, liquified
Formula: NH3
NFPA 30/OSHA Classification: n/a
DOT Class: Class 2.2, Non-flammable compressed gas
Shipping Label: NONFLAMMABLE GAS
ID No: UN 1005
CAS No: 7664-41-7
Statement of Hazards: Corrosive. May be an explosive hazard in a confined space.
Emergency Response Personal Protective Equipment: Wear special protective clothing and positive pressure self-contained breathing apparatus. Butyl rubber, Teflon, or Viton barrier recommended.
Spill or Leak Procedures: Releases may require isolation or evacuation. Stop or control the leak, if this can be one without undue risk. Use water spray to cool, absorb, and disperse vapors, and protect personnel. Approach release from upwind.
Fire Fighting Procedures: Use water spray to keep fire-exposed containers cool. Extinguish fire using agent suitable for surrounding fire.
Health Hazards: Corrosive. Liquid and vapor will burn skin and eyes severly. Serious health hazard. May be harmful if inhaled. Irritating to eyes, skin, and respiratory system. Symptoms of exposure include pulmonary edema and convulsions. Liquid ammonia may cause frostbite. Aqueous solutions of ammonia have considerable vapor pressure and present hazards of gas and liquid.
Fire and Explosion Hazards: May be an explosion hazard in a confined space.
Physical Properties: Colorless gas with penetrating suffocation characteristic odor. Liquid released under pressure floats and boils on water. Forms aqueous solutions with high vapor pressure.
Transport Information
Hazmat Placards are required for the transportation of ammonia or anhydrous ammonia. In the US, the Department of Transportation classifies ammonia as a hazard class 2.2 non-flammable gas. Internationally, ammonia is classified as a hazard class 2.3 poisonous gas.
| Classification | UN Number | Hazard Class | Packing Class |
|---|---|---|---|
| DOT US Department of Transportation |
UN1005 | 2.2 | None |
| IMDG International Maritime Dangerous Goods |
UN1005 | 2.3 | None |
49 CFR §173.115 Class 2. Divisions
(b) Division 2.2 (non-flammable, nonpoisonous compressed gas—including compressed gas, liquefied gas, pressurized cryogenic gas, compressed gas in solution, asphyxiant gas and oxidizing gas). For the purpose of this subchapter, a non-flammable, nonpoisonous compressed gas (Division 2.2) means any material (or mixture) which,
- Exerts in the packaging a gauge pressure of 200 kPa (29.0 psig/43.8 psia) or greater at 20 °C (68 °F), is a liquefied gas or is a cryogenic liquid, and
- Does not meet the definition of Division 2.1 or 2.3.
Identification of Ammonia Refrigeration Piping and System Components
IIAR Bulletin No. 114 provides uniform guidelines for identyfing ammonia refrigeration piping and system components to promote safety, facilitate maintenance and provide vital information to emergency respoders. The bulletin provides further guidance as follows:
3.1 Piping System
A piping system includes all ammonia refrigerant piping and fittings, hand valves, control valves and other devices that are inclusive to the refrigeration lines. Pipe insulation is also considered part of the piping system. Pipe supports, hangers, brackets or other piping accessories are not considered part of the piping system.
3.2 System Components
System components include compressors and compressor units, condensers, receivers, thermosyphon vessels, recirculators, intercoolers, accumulators, transfer vessels, oil pots, evaporators, heat exchangers and any other component of the refrigeration system containing refrigerant that is not inclusive to the refrigeration lines comprising the piping system.
4.0 Identification System
4.1 Piping Markers
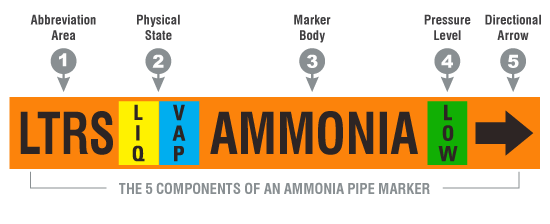
Piping markers in accordance with this guideline, are designed to identify the refrigerant contained within that piping segment (i.e., ammonia) including the physical state of the refrigerant, relative pressure level of the refrigerant and direction of flow.
The piping marker will be considered to have (5) sections:- marker body
- physical state section
- pressure level section
- abbreviation section
- directional arrow
What signage is required for an ammonia refrigeration machinery room?
Three categories of signage required for machinery rooms – machinerty room doors, alarm signs and stop switch / emergency ventilation. Identification signs are designed to provide a clear hazard warning for employees in food processing plants, mills and cold storage facilities utilizing ammonia refrigeration.
Machinery Room Door
According to Chapter 6 of ANSI/IIAR 2-2014 [1], machinery room entrances shall be provided with signage which (1) restricts the area to authorized personnel only and (2) indicates the proper NFPA 704 designation. In the informative section of IIAR 2-2014.
Appendix J suggests that all entrances to a machinery room include the following information:
- Refrigeration Machinery Room
- Authorized Personnel Only
- Caution – Ammonia R-717
- Caution – Eye and Ear Protection Required
- NFPA 704 – Ammonia Fire Diamond (Blue-3, Red-3, Yellow-0)
Alarm Signs
As a minimum requirement for facilities which properly have ammonia detection, signage shall be placed next to the actual audio / visual alarms that identify these alarms as part of the ammonia detection system [ANSI/IIAR 2-2014 §17.6].
With the following suggestive wording:
Warning – When Alarms Are Activated, Ammonia Has Been Detected
- Leave room immediately when alarms are activated.
- Do not enter except by emergency trained personnel only.
- Do not enter without personal protective equipment.
Additionally, Appendix J recommends that both the Refrigeration Stop Switch and Emergency Ventilation Switch be labeled as well.