Recommended Accessories
Frequently Purchased Together
Product Information
Details
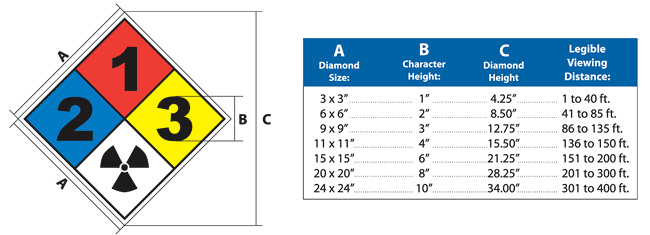
This Blank NFPA Diamond uses the NFPA rating system for chemical safety and emergency response. A 11" x 11" Blank NFPA Diamond is a useful device to help protect the health and safety of personnel, but is not an alternative for required protective measures for eliminating or abating hazards.
About InfiniStick™ Labels
We engineered our InfiniStick™ labels for maximum adhesiveness and durability. InfiniStick™ labels are made with Brimar’s specially formulated adhesive and ultra-durable vinyl and can withstand the most challenging conditions without peeling off. Safe for use between -20° to 176° F and capable of sticking to a wide range of smooth and rough surfaces, InfiniStick™ labels are ideal for nearly any application.
InfiniStick™ labels adhere to a wide range of surfaces, making them perfect for use outdoors, in industrial settings, on machines, containers, vehicles, and more. For maximum adhesion, simply wipe the surface clean, remove the film from the label, and stick.
Thanks to their durability and versatility, InfiniStick™ labels will remain in place and effective for years, saving you money compared to standard labels, which must be replaced more frequently. Whether your label contains a safety warning, hazard rating, or any other directive, you can count on the resilience of labels made with InfiniStick™ technology.
Compliance
NFPA 704 Signs & Labels
This document was last updated on 04/11/2013 using NFPA 704 2012 Edition.
- The NFPA 704 diamond system is intended to provide basic information to fire fighting, emergency and other personnel. This standard provides a readily recognized, easily understood system for identifying specific hazards and their severity using spatial, visual, and numerical methods to describe in simple terms the relative hazards of a material. These placards act as an immediate warning system for emergency service personnel, addressing health, flammability, instability, and special hazards that may be present, acute exposures that are most likely to occur as a result of fire, spill, or similar emergencies.
- NFPA 704 Hazardous Materials Identification System
Signs must be in locations approved by the authority having jurisdiction and as a minimum must be posted at the following locations:- Two exterior walls or enclosures containing a means of access to a building or facility.
- Each access to a room or area.
- Each principal means of access to an exterior storage area.
- If there are numerous areas where the emergency personnel could enter, then, there should be numerous signs covering those areas.
- Position NFPA Diamond signs on stationary containers and above-ground tanks and at entrances to locations where hazardous materials are stored, dispensed, used or handled in quantities that require an operational permit. The purpose of these signs is to assist first responders in recognizing and identifying possible hazards, thus they should be placed as to be readily visible with respect to location and size.
- Where can I find the NFPA 704 ratings for my chemicals?
(health, flammability, instability, and special hazard information such as oxidizers, water reactivity, or simple asphyxiant gases.) The best source for the NFPA 704 ratings of a material is the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), which can be obtained from the supplier of the material. The NFPA 704 ratings usually can be located in Section 16 of the MSDS. Other sources are reference material including the NFPA Fire Protection Guide on Hazardous Materials, and many other reference books and data bases on hazardous materials.
Why should the NFPA 704 Rating System be used?
- The 704 rating system is applicable to industrial, commercial, and institutional facilities that manufacture, process, use, or store hazardous materials. Please note this standard is not applicable to transportation (DOT) or for use by the general public.
- This standard objectives are, as stated by NFPA:
- These signs provide an appropriate signal or alert for the protection of both public and private emergency response personnel.
- To assist in planning for effective fire and emergency control operations, including clean-up.
- To assist all designated personnel, engineers, plant, and safety personnel in evaluating hazards.
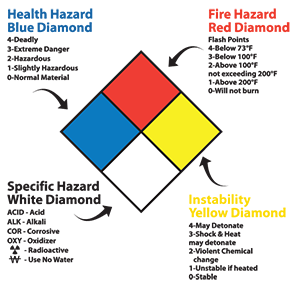
Understanding the NFPA 704 sign?
- This is diamond-shaped sign with four smaller quadrants/diamonds inside. One diamond is blue, one is red, one is yellow and one is white, as shown on image. The diamond-shaped signs use the four color-coded categories to give at a glance a general idea of the hazards that personnel or observers are exposed to in any specific area.
- The number in each inner quadrant represents the hazard rating for each of the 3 categories. Each material is assigned a rating in these three categories: health (blue), flammability (red), and instability (yellow). The white box is reserved for special hazards such as water reactivity, oxidizers or simple asphyxiant gases. The health, flammability, and instability ratings of a material vary according to its physical and chemical characteristics. The ratings are 4, 3, 2, 1, or 0, with 4, indicating severe hazard or extreme danger, to 0, indicating no required warning is necessary. Each rating is described on the image to the side.
Hazard Category: HEALTH (Blue)
The degree of hazard shall indicate to fire-fighting and emergency response personnel one of the following:
- They can work safely in the area only with specialized protective equipment.
- They can work safely in the area with suitable respiratory protective equipment.
- They can work safely in the area with ordinary clothing.
Degrees of Hazard. The degrees of health hazard shall be ranked according to the probable severity of the effects of exposure to emergency response personnel.
Rating 4: Materials that, under emergency conditions, can be lethal.
- Gases whose LC50 for acute inhalation toxicity is less than or equal to 1000 parts per million (ppm).
- Any liquid whose saturated vapor concentration at 20°C (68°F) is equal to or greater than 10 times its LC50 for acute inhalation toxicity, if its LC50 is less than or equal to 1000 ppm.
- Dusts and mists whose LC50 for acute inhalation toxicity is less than or equal to 0.5 milligram per liter (mg/L).
- Materials whose LD50 for acute dermal toxicity is less than or equal to 40 milligrams per kilogram (mg/kg).
- Materials whose LD50 for acute oral toxicity is less than or equal to 5 mg/kg.
Rating 3: Materials that, under emergency conditions, can cause serious or permanent injury.
- Gases whose LC50 for acute inhalation toxicity is greater than 1000 ppm but less than or equal to 3000 ppm.
- Any liquid whose saturated vapor concentration at 20°C (68°F) is equal to or greater than its LC50 for acute inhalation toxicity, if its LC50 is less than or equal to 3000 ppm, and that does not meet the criteria for degree of hazard 4.
- Dusts and mists whose LC50 for acute inhalation toxicity is greater than 0.5 mg/L but less than or equal to 2 mg/L.
- Materials whose LD50 for acute dermal toxicity is greater than 40 mg/kg but less than or equal to 200 mg/kg/.
- Materials that are corrosive to the respiratory tract.
- Materials that are corrosive to the eye or cause irreversible corneal opacity.
- Materials that are corrosive to skin.
- Cryogenic fluids that cause frostbite and irreversible tissue damage.
- Compressed liquefied gases with boiling points at or below −55°C (−66.5°F) that cause frostbite and irreversible tissue damage.
- Materials whose LD50 for acute oral toxicity is greater than 5 mg/kg but less than or equal to 50 mg/kg
Rating 2: Materials that, under emergency conditions, can cause temporary incapacitation or residual injury.
- Gases whose LC50 for acute inhalation toxicity is greater than 3000 ppm but less than or equal to 5000 ppm.
- Any liquid whose saturated vapor concentration at 20°C (68°F) is equal to or greater than one-fifth its LC50 for acute inhalation toxicity, if its LC50 is less than or equal to 5000 ppm, and that does not meet the criteria for either degree of hazard 3 or degree of hazard 4.
- Dusts and mists whose LC50 for acute inhalation toxicity is greater than 2 mg/L but less than or equal to 10 mg/L.
- Materials whose LD50 for acute dermal toxicity is greater than 200 mg/kg but less than or equal to 1000 mg/kg.
- Compressed liquefied gases with boiling points between −30°C (−22°F) and −55°C (−66.5°F) that can cause severe tissue damage on contact, depending on duration of exposure.
- Materials that are respiratory irritants.
- Materials that cause severe but reversible irritation to the eyes or lacrimators.
- Materials that are primary skin irritants or sensitizers Materials whose LD50 for acute oral toxicity is greater than 50 mg/kg but less than or equal to 500 mg/kg.
Rating 1: Materials that, under emergency conditions, can cause significant irritation.
- Gases and vapors whose LC50 for acute inhalation toxicity is greater than 5000 ppm but less than or equal to 10,000 ppm.
- Dusts and mists whose LC50 for acute inhalation toxicity is greater than 10 mg/L but less than or equal to 200 mg/L.
- Materials whose LD50 for acute dermal toxicity is greater than 1000 mg/kg but less than or equal to 2000 mg/kg.
- Materials that cause slight to moderate irritation to the respiratory tract, eyes, and skin.
- Materials whose LD50 for acute oral toxicity is greater than 500 mg/kg but less than or equal to 2000 mg/kg.
Rating 0: Materials that, under emergency conditions, would offer no hazard beyond that of ordinary combustible materials.
- Gases and vapors whose LC50 for acute inhalation toxicity is greater than 10,000 ppm.
- Dusts and mists whose LC50 for acute inhalation toxicity is greater than 200 mg/L.
- Materials whose LD50 for acute dermal toxicity is greater than 2000 mg/kg.
- Materials whose LD50 for acute oral toxicity is greater than 2000 mg/kg.
- Materials that are essentially nonirritating to the respiratory tract, eyes, and skin.
Hazard Category: FLAMMABILITY (Red)
Because many materials will burn under one set of conditions but will not burn under others, the form or condition of the material shall be considered, along with its inherent properties.
Degrees of Hazard. The degrees of flammability hazard shall be ranked according to the susceptibility of materials to burning.
Rating 4: Materials that rapidly or completely vaporize at atmospheric pressure and normal ambient temperature or that are readily dispersed in air and burn readily.
- Flammable gases.
- Flammable cryogenic materials.
- Any liquid or gaseous material that is liquid while under pressure and has a flash point below 22.8°C (73°F) and a boiling point below 37.8°C (100°F) (i.e., Class IA liquids) Materials that ignite spontaneously when exposed to air.
- Solids containing greater than 0.5 percent by weight of a flammable or combustible solvent are rated by the closed cup flash point of the solvent.
Rating 3: Liquids and solids (including finely divided suspended solids) that can be ignited under almost all ambient temperature conditions. Materials in this degree produce hazardous atmospheres with air under almost all ambient temperatures or, though unaffected by ambient temperatures, are readily ignited under almost all conditions. See Annex D for more information on ranking of combustible dusts.
- Liquids having a flash point below 22.8°C (73°F) and a boiling point at or above 37.8°C (100°F) and those liquids having a flash point at or above 22.8°C (73°F) and below 37.8°C (100°F) (i.e., Class IB and Class IC liquids)
- Finely divided solids, typically less than 75 micrometers (μm) (200 mesh), that present an elevated risk of forming an ignitible dust cloud, such as finely divided sulfur.
- National Electrical Code Group E dusts (e.g., aluminum, zirconium, and titanium), and bis-phenol A.
- Materials that burn with extreme rapidity, usually by reason of self-contained oxygen (e.g., dry nitrocellulose and many organic peroxides)
- Solids containing greater than 0.5 percent by weight of a flammable or combustible solvent are rated by the closed cup flash point of the solvent.
Rating 2: Materials that must be moderately heated or exposed to relatively high ambient temperatures before ignition can occur. Under normal conditions, these materials would not form hazardous atmospheres with air, but under high ambient temperatures or under moderate heating they could release vapor in sufficient quantities to produce hazardous atmospheres with air. Materials in this degree also include finely divided suspended solids that do not require heating before ignition can occur. See Annex D for more information on ranking of combustible dusts.
- Liquids having a flash point at or above 37.8°C (100°F) and below 93.4°C (200°F) (i.e., Class II and Class III A liquids)
- Finely divided solids less than 420 μm (40 mesh) that present an ordinary risk of forming an ignitible dust cloud.
- Solid materials in a flake, fibrous, or shredded form that burn rapidly and create flash fire hazards, such as cotton, sisal, and hemp.
- Solids and semisolids that readily give off flammable vapors.
- Solids containing greater than 0.5 percent by weight of a flammable or combustible solvent are rated by the closed cup flash point of the solvent.
Rating 1: Materials that must be preheated before ignition can occur. Materials in this degree require considerable preheating, under all ambient temperature conditions, before ignition and combustion can occur. Materials in this degree also include finely divided suspended solids that do not require heating before ignition can occur. See Annex D for more information on ranking of combustible dusts.
Rating 0: Materials that will not burn under typical fire conditions, including intrinsically noncombustible materials such as concrete, stone, and sand.
- Materials that will not burn in air when exposed to a temperature of 816°C (1500°F) for a period of 5 minutes in accordance with ASTM D 6668, Standard Test Method for the Discrimination Between Flammability Ratings of F = 0 and F = 1
Hazard Category: INSTABILITY (Yellow)
The degree of instability hazard shall indicate to firefighting and emergency personnel whether the area shall be evacuated, whether a fire shall be fought from a protected location, whether caution shall be used in approaching a spill or fire to apply extinguishing agents, or whether a fire can be fought using normal procedures.
Degrees of Hazard. The degrees of hazard shall be ranked according to ease, rate, and quantity of energy release of the material in pure or commercial form.
Rating 4: Materials that in themselves are readily capable of detonation or explosive decomposition or explosive reaction at normal temperatures and pressures.
- Materials that are sensitive to localized thermal or mechanical shock at normal temperatures and pressures.
- Materials that have an instantaneous power density (product of heat of reaction and reaction rate) at 250°C (482°F) of 1000 W/mL or greater.
Rating 3: Materials that in themselves are capable of detonation or explosive decomposition or explosive reaction but that require a strong initiating source or must be heated under confinement before initiation.
- Materials that have an instantaneous power density (product of heat of reaction and reaction rate) at 250°C (482°F) at or above 100 W/mL and below 1000 W/mL.
- Materials that are sensitive to thermal or mechanical shock at elevated temperatures and pressures.
Rating 2: Materials that readily undergo violent chemical change at elevated temperatures and pressures.
- Materials that have an instantaneous power density (product of heat of reaction and reaction rate) at 250°C (482°F) at or above 10 W/mL and below 100 W/mL.
- Materials that exhibit an exotherm at temperatures less than or equal to 150°C (302°F) when tested by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC)
Rating 1: Materials that in themselves are normally stable but that can become unstable at elevated temperatures and pressures.
- Materials that have an instantaneous power density (product of heat of reaction and reaction rate) at 250°C (482°F) at or above 0.01 W/mL and below 10 W/mL.
- Materials that exhibit an exotherm at temperatures greater than 150°C (302°F) but less than or equal to 300°C (604°F) when tested by differential scanning calorimetry.
Rating 0: Materials that in themselves are normally stable, even under fire conditions.
- Materials that have an instantaneous power density (product of heat of reaction and reaction rate) at 250°C (482°F) below 0.01 W/mL.
- Materials that exhibit an exotherm at temperatures greater than 300°C (604°F) but less than or equal to 500°C (932°F) when tested by differential scanning calorimetry.
- Materials that do not exhibit an exotherm at temperatures less than or equal to 500°C (932°F) when tested by differential scanning calorimetry.
Hazard Category: SPECIAL HAZARDS (White)
Only W with a line thru (water reactivity), OX (oxidizers) and SA (simple asphyxiant gases) are officially part of the NFPA 704 2012 standard.
8.2 Symbols. Special hazards shall be represented by a spatial arrangement denoted by symbols always at the six o'clock position.
- 8.2.1* Materials that react violently or explosively with water (i.e., water reactivity rating 2 or 3) shall be identified by the letter "W" with a horizontal line through the center ( W )
- 8.2.2* Materials that possess oxidizing properties shall be identified by the letters "OX"
- 8.2.3* For chemicals requiring both "special hazard" symbols (i.e., W and OX), the W shall be displayed inside the special hazards quadrant, and the OX shall be displayed directly below or adjacent to the special hazards quadrant.
- 8.2.4* Materials that are simple asphyxiant gases shall be permitted to be identified with the letters "SA" and shall be limited to the following gases: nitrogen, helium, neon, argon, krypton, and xenon.
Official Recognized NFPA 704 Symbols
- W (with line accross): Materials that react violently or explosively with water.
- OX: Materials that possess oxidizing properties.
Optional Symbol
- SA: Materials that are simple asphyxiant gases (includes nitrogen, helium, neon, argon, krypton, and xenon).
Non-Standard Symbols
User-defined symbols or markings below must be placed outside the NFPA "diamond". Appropriate training and communication addressing these other markings are essential. Other special hazard symbols (beyond OX and W ) should not be considered to be part of the NFPA 704 hazard rating system. In many cases, the hazards represented by these symbols are already considered in the health, flammability, or instability rating categories. In addition, because these additional symbols are not defined by the standard, emergency responders might not recognize their significance.
- COR: Materials that will not burn.
- ACID and ALK (Alkali) to be more specific.
- BIO: Biological Hazard.
- POI: Poisonous Material (e.g. strychnime)
- CYL or CRYO: Cryogenic Material (e.g. liquid nitrogen)
- Radioactive trefoil: Radioactive materials. (e.g. plutonium, uranium)
- The field may also be left blank if no special hazards are present.